The cost allocation in the form of depreciation will ultimately ensure that the final value of the asset appearing in the financial statement will reflect its true and fair current value. Understanding and utilizing the Depreciation Tax Shield effectively can lead to significant tax savings and is an important part of financial how to invoice us planning for businesses. A 25 % depreciation for plant and machinery is available on accelerated depreciation basis as Income tax exemption. Assume that the corporate tax is paid one year in arrear of the periods to which it relates, and the first year’s depreciation allowance would be claimed against the profits of year 1.
What is a Section 179 Deduction?
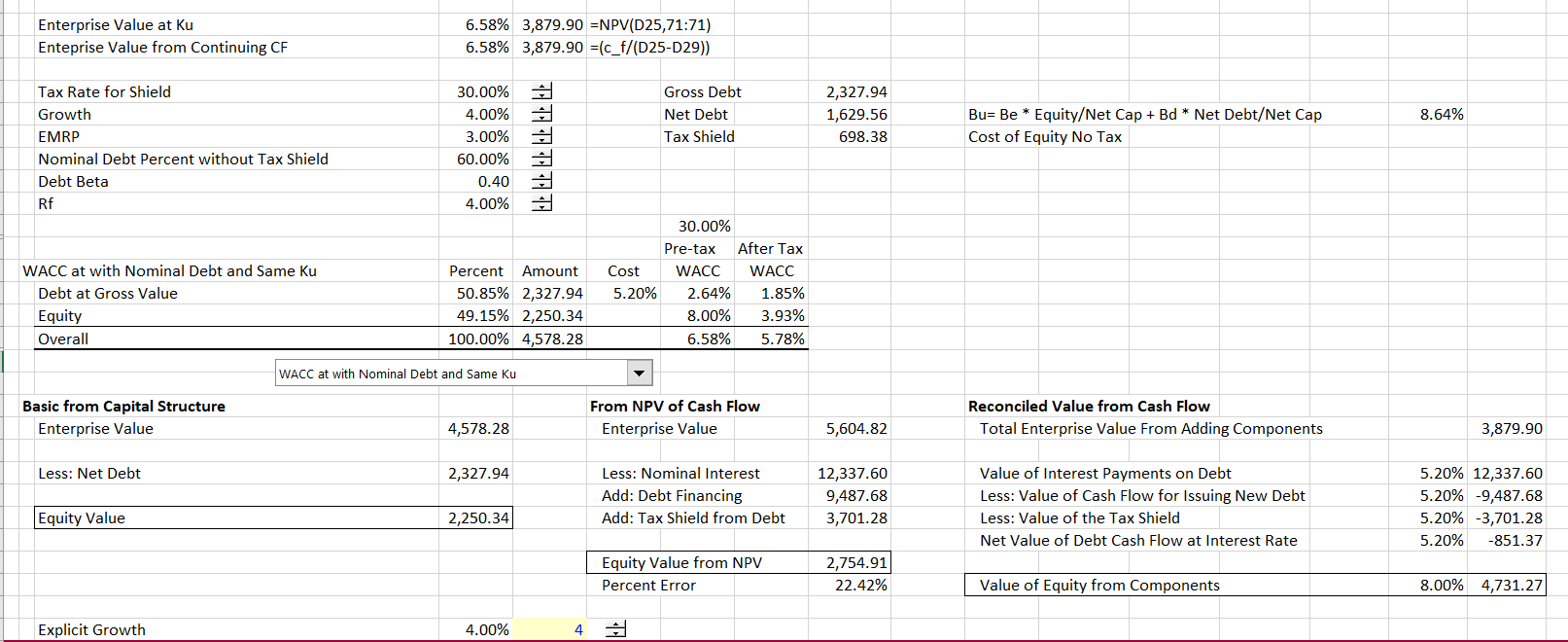
The Debt used in the purchase creates Interest Expense that reduces the acquired Company’s Tax bill. Below, we take a look at an example of how a change in the Depreciation method can have an impact on Cash Flow (and thus Valuation). In Case we don’t take the Depreciation into account, then the Total Tax to be paid by the company is 1381 Dollar.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
The concept of annual depreciation tax shield is identified as an important factor during financial decision-making by the management in case the business is highly capital-intensive. The business operation will involve the use of assets of larger value resulting in a substantial amount of depreciation being deducted from the taxable income. Therefore, it is important to understand the formula used to calculate depreciation tax shield, as given below. Do you know that using smart ways to keep track of how things lose value can actually help a company save money on taxes and improve its financial situation? By using a strategy called depreciation, businesses can take advantage of tax benefits and make their money work smarter for them.
What are the benefits?
Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. The difference in EBIT amounts to $2 million, entirely attributable to the depreciation expense. The real cash outflow stemming from capital expenditures has already occurred, however in U.S. GAAP accounting, the expense is recorded and spread across multiple periods.
Depreciation Tax Shield Formula
D&A is embedded within a company’s cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating expenses, so the recommended source to find the total value is the cash flow statement (CFS). We note from above that the Tax Shield has a direct impact on the profits as net income will come down if depreciation expense is increasing, resulting in less tax burden. It is the method companies use to allocate the cost of an asset, which may be machinery, building, etc., throughout its useful life. This is done because every asset is subject to a fall in value during usage due to continuous wear and tear.
- There are a variety of deductions that can shield a company (or Individual) from paying Taxes.
- If we add up all the taxes, the amount is substantial, which could be saved if the business had charged depreciation in the income statement.
- This amount in the profit and loss statement brings down the total revenue earned by the business, thus successfully leading to lower tax payments.
- It is necessary to understand the importance of the concept of depreciation tax shield equation in the corporate environment as a temporary benefit to save taxes.
- Conversely, a services business may have few (if any) fixed assets, and so will not have a material amount of depreciation to employ as a tax shield.
A depreciation tax shield is a tax reduction technique under which depreciation expense is subtracted from taxable income. The amount by which depreciation shields the taxpayer from income taxes is the applicable tax rate, multiplied by the amount of depreciation. This tax shield can cause a substantial reduction in the amount of taxable income, so many organizations prefer to use accelerated depreciation to accelerate its effect. Accelerated deprecation charges the bulk of an asset’s cost to expense during the first half of its useful life. The term “Tax Shield” refers to the deduction allowed on the taxable income that eventually results in the reduction of taxes owed to the government. The formula for tax shields is very simple, and it is calculated by first adding the different tax-deductible expenses and then multiplying the result by the tax rate.
This stipulation can reduce your tax bill more significantly than if you were to depreciate your assets over a prolonged period. You can use this Section 179 deduction calculator to estimate how much tax you could save under Section 179. All you need to do is input the details of the equipment, select your tax bracket from the options available, and click on the “Calculate” button to compute the savings. Tax shields are an important aspect of business valuation and vary from country to country. Their benefits depend upon the taxpayer’s overall tax rate and cash flow for the given tax year. In addition, governments often create tax shields to encourage certain behavior or investment in certain industries or programs.
It also provides incentives to those interested in purchasing a home by providing a specific tax benefit to the borrower. The recognition of depreciation causes a reduction to the pre-tax income (or earnings before taxes, “EBT”) for each period, thereby effectively creating a tax benefit. The taxes saved due to the Interest Expense deductions are the Interest Tax Shield.
As opposed to deducing the costs of assets over several years, you can opt to deduct the asset from your tax bill in the year in which it was bought. As such, Section 179 is ideal for organizations that are looking to maximize tax savings. Essentially, the business writes off the full cost of any assets in the year they were bought as opposed to spreading the depreciation over the lifespan of the asset. Meanwhile, the company maintains its own depreciation calculations for financial statement reporting, which are more likely to use the straight-line method of depreciation.
By using accelerated depreciation, a taxpayer can defer the recognition of taxable income until later years, thereby deferring the payment of income taxes to the government. The tax shield is a very important aspect of corporate accounting since it is the amount a company can save on income tax payments by using various deductible expenses. The higher the savings from the tax shield, the higher the company’s cash profit. The extent of tax shield varies from nation to nation, and their benefits also vary based on the overall tax rate. Companies using accelerated depreciation methods (higher depreciation in initial years) are able to save more taxes due to higher value of tax shield. A tax shield is a reduction of taxable income due to decreasing it by deductible expenses like interest, amortization, and depreciation.





